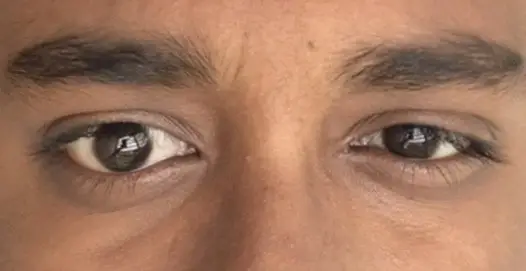
The human body is complex, and there can be many reasons why one eye may appear smaller than the other. It is important to note that some level of asymmetry is natural and can be completely normal. However, if the difference in size is significant or noticeable, it could be a sign of an underlying health issue. In this article, we will explore some of the most common causes of a smaller left eye and provide some insight into when it may be necessary to see a doctor.
- Genetics
One of the most common causes of an asymmetrical appearance in the eyes is simply genetics. It is not uncommon for certain facial features to be inherited from one or both parents, and this can include the size and shape of the eyes. In many cases, this type of asymmetry is nothing to worry about and does not pose any risks to a person’s health. However, if there is a significant difference in size between the eyes, it may be worth speaking to a doctor to rule out any underlying conditions.
- Trauma
Another possible cause of a smaller left eye is trauma. If you have suffered an injury to your left eye or the surrounding area, it could cause swelling or damage that could affect its appearance. For example, if you have been hit in the face, this could cause swelling around the eye socket, making the left eye appear smaller than the right. In some cases, the damage may be severe enough to affect vision, so it is important to seek medical attention if you have experienced any trauma to the eye.
- Ptosis
Ptosis is a medical condition that affects the muscles that control the eyelids. It can cause one or both eyelids to droop, which can make the eye appear smaller than normal. In some cases, ptosis can also cause other symptoms, such as difficulty closing the eye or vision problems. There are several different causes of ptosis, including muscle weakness, nerve damage, and certain medical conditions, so it is important to see a doctor if you think you may have this condition.
- Anisometropia
Anisometropia is a condition that affects the eyes’ ability to focus correctly. It occurs when one eye has a significantly different refractive error than the other, which can cause differences in the size and shape of the eyes. In some cases, anisometropia can also cause other symptoms, such as headaches or double vision. Treatment options for anisometropia may include glasses or contact lenses, or in some cases, surgery.
- Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland. It can cause a wide range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight loss, and anxiety. It can also affect the eyes, causing them to bulge out or appear to be different sizes. In some cases, Graves’ disease can also cause double vision or other vision problems. Treatment options for Graves’ disease may include medication, surgery, or radioactive iodine therapy.
- Orbital Tumor
An orbital tumor is a type of growth that occurs in or around the eye socket. It can cause a wide range of symptoms, including a smaller or asymmetrical appearance in the eyes. Other symptoms of an orbital tumor may include pain, double vision, or a feeling of pressure behind the eyes. Treatment options for an orbital tumor may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
In conclusion, there are several potential reasons why your left eye may appear smaller than your right eye. While some level of asymmetry is natural and can be completely normal, significant differences in size or shape could be a sign of an underlying health issue. If you are concerned about your eye appearance or have other symptoms such as vision changes, pain or double vision, it is important to speak with a doctor or