There are dozens of device interfaces, connectors, and cables on the market. While you can tell apart most of them, a handful of connectors manage to look the same even though they have very different functionalities.
As a primary example, the Micro HDMI connector resembles the Micro USB connector’s size, which causes plenty of confusion among consumers who don’t have the knowledge of connector types. Considering their use-case is vastly different, you may end up buying the wrong cable from the store.
If you are unaware of which cables are used for data transfer, device charging, or audiovisual output, check out this information guide to learn more. We have talked about the differences between Micro USB and Micro HDMI in detail.
Key Differences Between Micro USB and Micro HDMI
Introduced in 2007 as part of the USB 2.0 standard, Micro USB is predominately found on older mobile phones, tablets, cameras, wireless headphones, and hundreds of different devices for data transfer and power delivery.
As its name suggests, Micro USB is smaller than the regular Type-A USB connectors found on computers, smart TVs, and many other devices.
At 6.85 x 1.8 mm, Micro USB is also smaller and shaped differently than its Mini USB counterpart, with a sloping top and flat bottom. It has a transfer rate of 480 Mbit/s, and it can withstand 10000+ connect-disconnect cycles.
Furthermore, its inclusion of USB On The Go (USB OTG) allows users to connect regular USB devices to smartphones or tablets using a passive adapter.
On the other hand, Micro HDMI or HDMI Type-D is a compact version of the standard Type-A HDMI interface, released in 2009 with the HDMI 1.4 standard. While its 5.83 x 2.20 mm dimensions make it much smaller than the original connector, it consists of the same 19 pins for connection.
Thus, you can use it to get an uncompressed video/audio feed from an HDMI compliant source device to a television, projector, monitor, or digital sound system.
Micro HDMI made its initial debut in the market with the Motorola Droid X in 2010, giving users the option to connect the phone to a television or monitor over a Micro HDMI to Type-A HDMI cable.
However, its use is relatively niche in the present, mostly making appearances on action cameras, handheld PCs, etc.
The newly launched Sony Xperia Pro smartphone also has a Micro HDMI receptacle, allowing professional photographers to use it as a 4K viewfinder for cameras.
Therefore, Micro USB and Micro HDMI aren’t the same even though they look almost identical to average consumers. Micro USB’s primary function is to enable charging and data transfer on devices, whereas Micro HDMI’s only role is to transmit video and audio data from a compact source device to a display or speaker.
See – What Is An HDMI Cable With Ethernet?
How does USB Type-C Compare to Micro USB?
USB-C is the successor to the Type-A USB interface, and it’s better than Micro USB in every aspect. It consolidates several functionalities in one connector, including fast power delivery, high-speed data transfer, display and audio output, etc.
One of the key changes in USB-C is its physical construction. Unlike the Micro USB plug, it doesn’t have protruding hooks on one side and is reversible (can be inserted either way) due to its symmetrical shape. It’s also more durable and has a better connect-disconnect cycle than Micro USB.
On a more technical side of things, USB-C connectors have a theoretical data delivery speed of up to 20 Gbps and can provide up to 100 W of power. On top of that, USB 3.1 Type-C can transmit 4K@60Hz video output, making it a suitable connector over Micro HDMI in devices that don’t have much space for a separate jack.
It’s also worth noting that USB-C is adaptive to legacy USB connectors. For example, you can use a passive Type-C to Type-A cable or adapter to connect devices with different USB plugs or receptacles.
In 2021, manufacturers have finally embraced USB-C as the “one-size-fits-all” approach, replacing the aging Micro USB connectors smartphones, tablets, wearables, cameras, headphones, game controllers, VR headsets, and even the reigning Type-A port on higher-end Windows and Mac laptops.
Considering the versatility it offers in contrast to Micro USB, USB Type-C is the wunderkind of USB technology, at least for now.
How do you Tell Apart Mini USB, Micro USB, & USB-C?
The Mini USB, Micro USB, and USB-C are vastly different from each other in size, shape, and functionality. Thus, it isn’t really that difficult to distinguish one from another.
If you have a very old digital camera, MP3 player, or a feature phone from circa 2005, chances are it’s using the Mini USB or Type-B connector. It was pitched as a smaller version of the original Type-A connector, except that it didn’t carry the same specifications. Plus, the connector had several durability issues right from the beginning, which is why Micro USB took its place after two years.
Speaking of Micro USB, it’s still found on some entry-level smartphones, tablets, cameras, speakers, game controllers, wireless headphones, and several other devices. The connector has three versions: Micro-A, Micro-B, and Micro-B SuperSpeed. Out of all the variants, the Micro-B connector is the most common solution.
As we mentioned earlier, USB Type-C is currently the only practical solution to replacing almost all types of connectors and cables. It has dozens of use-cases, including bidirectional data transfer, AV output, and power delivery.
If you need more insight into the physical aspects of the different USB connectors, consider taking a closer look at the image below.
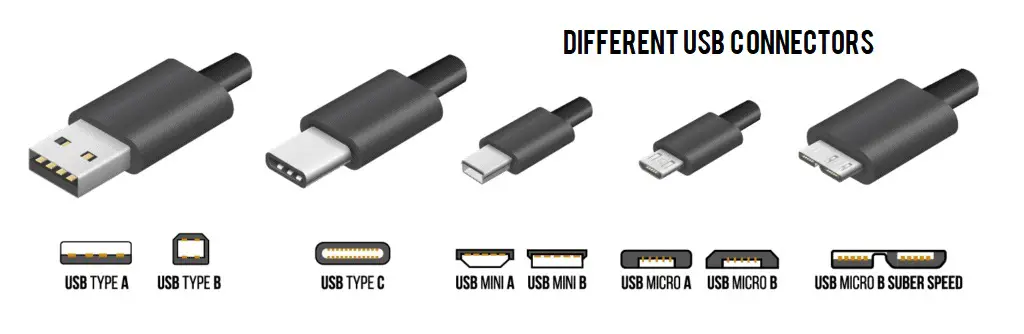
How do you Tell Apart Type-A, Mini, and Micro HDMI Connectors?
If you are in the market for a new HDMI cable, you will mostly come across the ones with the Type-A HDMI plug on both ends. It’s the standard for TVs, Blu-ray players, PCs, laptops, game consoles, soundbars, and other AV devices.
The Mini HDMI or Type-C (not to be confused with USB Type-C) connectors are common on professional-grade cameras and other smaller-sized products. It holds the middle ground between Type-A and Micro HDMI in size, and its benefits are parallel to the full-sized port.
The same goes for the Micro HDMI or Type-D connector, which is almost identical to USB Micro-B in size. As discussed in the previous section, Micro HDMI is found on handheld computers, ultra-slim notebooks, camera viewfinders, and older phones/tablets.
The below picture visually describes the differences between the Type-A, Mini, and Micro HDMI plugs and receptacles. Note that the Type-B and Type-E connectors are not seen in consumer products.
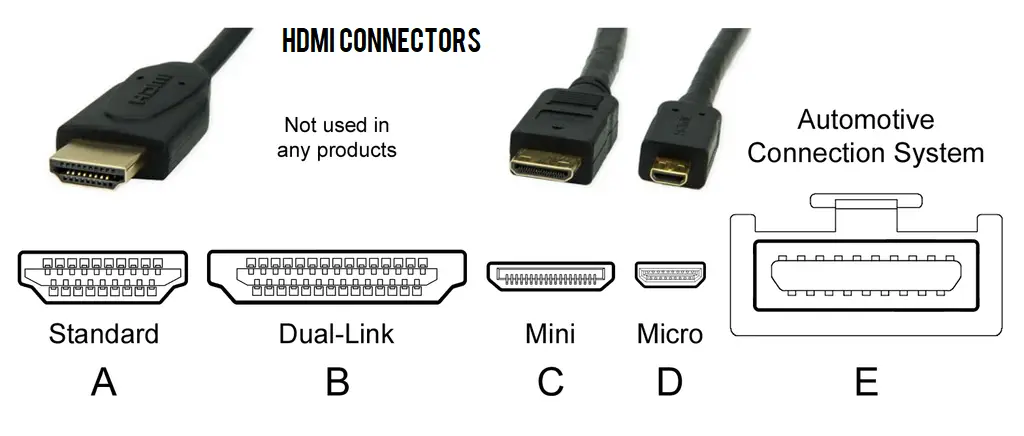
Also, Check – HDMI STB vs DVI vs MHL vs ARC – Which Port to Use?
To Conclude
That’s roughly everything you need to know about the differences between Micro USB and Micro HDMI. We have also compared them with other USB and HDMI connector types so that you know what to purchase for your particular usage.
Thanks to the benefits of USB-C, we are more than ready to wave goodbye to Micro USB and Micro HDMI. But they still do deserve your attention, considering you may have older devices that use the legacy interfaces. Plus, all the USB and HDMI connectors are cross-compatible, so it’s good to know about the types in case you ever need to buy a specific cable or adapter.
